前言
由于二叉树是一种递归定义的数据结构,采用递归的方式去遍历是一种非常简洁方便的做法,但是如果要求使用非递归的方式去遍历整棵二叉树则必须使用辅助的空间。以下分别实现二叉树的前序、中序、后序以及层序的遍历算法。约定二叉树的基本结构如下:
1 | template <typename DataType> |
前序非递归遍历
前序遍历的顺序为根->左->右,因此在使用辅助栈时,结合栈的先进后出特性,为了让左子树能在右子树之前弹出,我们可以先把右子节点先压入栈中,然后就可以保证左子节点先弹出,实现代码如下所示:
1 |
|
中序非递归遍历
中序遍历的顺序为左->根->右,因此在左子树被访问前根才能被访问,因此需要一直压栈最左,然后弹栈压入栈顶的右子节点,代码实现如下:
1 |
|
后序非递归遍历
后序遍历的顺序为左->右->根,由于根是最后访问,我们可以考虑前序遍历的思路,最后镜像结果即可。后序遍历的镜像访问顺序为根->右->左,和前序遍历的顺序只是访问左右的结果不同,因此可以将前序代码稍作调整即可用于后序遍历,代码如下:
1 |
|
层序遍历
层序遍历类似于广度优先搜索(BFS),此时一般使用队列来辅助存储,其思路可以借鉴前序遍历思路,只是弹出(出队)顺序略有不同,只需对前序代码稍作修改即可,具体代码见下:
1 |
|
如果要考虑分层输出的问题,则需要增加几个标识变量用来标识某一层的结束。由于已知第一层只有一个根节点,通过这个已知条件就可以推算下一层结束节点,换句话来说是一层最后的一个节点的右子节点是下一层的最后一个节点。将上述层序代码稍作变形就可以得到支持分层的代码:
1 |
|
代码测试
手动做出如下图的一棵二叉树:图片来源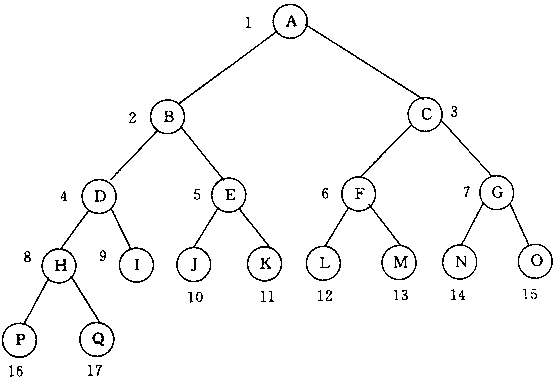
测试代码如下所示:
1 |
|